Overview and architecture
NGINX as a Service for Azure is a service offering that is tightly integrated into Microsoft Azure public cloud and its ecosystem, making applications fast, efficient, and reliable with full lifecycle management of advanced NGINX traffic services. NGINXaaS for Azure is available in the Azure Marketplace.
NGINXaaS for Azure is powered by NGINX Plus, which extends NGINX Open Source with advanced functionality and provides customers with a complete application delivery solution. Initial use cases covered by NGINXaaS include L4 TCP and L7 HTTP load balancing and reverse proxy which can be managed through various Azure management tools. NGINXaaS allows you to provision distinct deployments as per your business or technical requirements.
NGINXaaS handles the NGINX Plus license management automatically.
The key capabilities of NGINXaaS for Azure are:
- Simplifies onboarding by leveraging NGINX as a service.
- Lowers operational overhead in running and optimizing NGINX.
- Simplifies NGINX deployments with fewer moving parts (edge routing is built into the service).
- Supports migration of existing NGINX configurations to the cloud with minimal effort.
- Integrates with the Azure ecosystem (Microsoft Entra, Azure Key Vault, and Azure Monitor).
- Addresses a wide range of deployment scenarios (HTTP reverse proxy, JWT authentication, etc).
- Adopts a consumption-based pricing to align infrastructure costs to actual usage by billing transactions using Azure.
- Supports end-to-end encryption from client to upstream server.
- Supports the following protocols: HTTPS, HTTP, HTTP/2, HTTP/3, TCP, QUIC, IMAP, POP3, and SMTP.
- Supports any type of message body for upstream and error status code responses, including text/plain, text/css, text/html, application/javascript, and application/json.
- NGINXaaS does not support IPv6 yet.
- NGINXaaS supports one public or private IP per deployment. NGINXaaS doesn’t support a mix of public and private IPs at this time.
- The IP address associated with an NGINXaaS deployment can’t be changed from public to private, or from private to public.
NGINXaaS for Azure is supported in the following regions:
| North America | South America | Europe | Asia Pacific |
|---|---|---|---|
| West Central US West US East US 2 West US 2 West US 3 East US Central US North Central US Canada Central |
Brazil South | West Europe North Europe Sweden Central Germany West Central UK West UK South |
Australia East Japan East Korea Central Southeast Asia Central India South India |
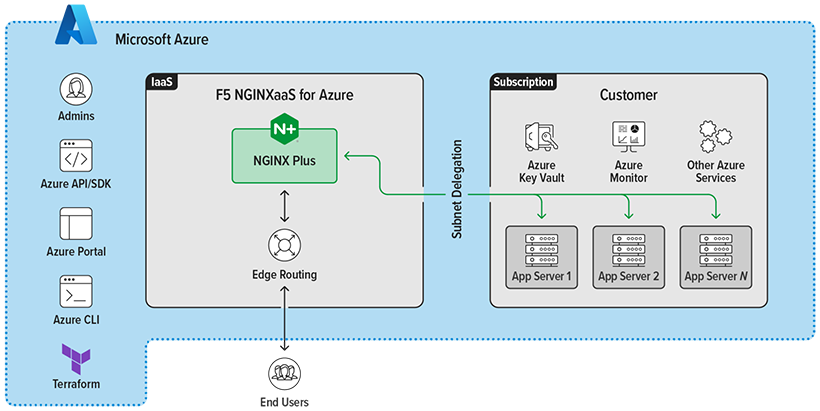
- Azure management tools (API, CLI, portal, terraform) work with NGINXaaS to create, update, and delete deployments
- Each NGINXaaS deployment has dedicated network and compute resources. There is no possibility of noisy neighbor problems or data leakage between deployments
- NGINXaaS can route traffic to upstreams even if the upstream servers are located in different geographies. See Known Issues for any networking restrictions.
- NGINXaaS supports request tracing. See the Application Performance Management with NGINX Variables blog to learn more about tracing.
- Supports HTTP to HTTPS, HTTPS to HTTP, and HTTP to HTTP redirects. NGINXaaS also provides the ability to create new rules for redirecting. See How to Create NGINX Rewrite Rules | NGINX for more details.
- NGINXaaS is deployed inside of your Azure network and can connect to your upstream application running in your ecosystem. Known networking limitations can be found in the Known Issues.
With the Standard V2 Plan, NGINXaaS uses the following redundancy features to keep your service available.
- We run at least two NGINX Plus instances for each deployment in an active-active pattern
- NGINX Plus is constantly monitored for health. Any unhealthy instances are replaced with new ones
- We use Azure Availability Zones to protect your deployment from local failures within an Azure region. We balance NGINX instances across the possible availability zones in supported regions
Note: If you are creating a public IP for your deployment, be sure to make them zone redundant to get the best uptime.
- NGINXaaS uses new Azure networking capabilities to keep end-user traffic private. A network security group ensures that the deployment is secured and inbound connections are allowed to the ports the NGINX service listens to.
- You can restrict access to NGINXaaS by defining restriction rules at the Network Security Group level or using NGINX’s access control list. To learn more, see the NGINX module ngx_http_access_module documentation.
- NGINXaaS deployment is automatically upgraded to receive security patches and the latest stable NGINX Plus version.
To get started, check the NGINX as a Service for Azure prerequisites